How to connect to MySQL and run select query is shown in this blog.
▼1. What is MySQL?
MySQL, the most popular Open Source SQL database management system, is developed, distributed, and supported by Oracle Corporation. MySQL is available on some cloud services such as Azure, AWS, Oracle etc.
▼2. Prerequisites
2-1. Install JDK
Install Java 8 openjdk x64 of zulu
mkdir -p /usr/lib/jvm/
cd /usr/lib/jvm/
sudo wget https://cdn.azul.com/zulu/bin/zulu8.66.0.15-ca-jdk8.0.352-linux_x64.tar.gz
sudo tar -xzvf zulu8.66.0.15-ca-jdk8.0.352-linux_x64.tar.gz
sudo mv zulu8.66.0.15-ca-jdk8.0.352-linux_x64 java-8-openjdk-linux_x64Set environment variables
Use vi editor like “vi ~/.bashrc” and add below in ~/.bashrc
export JAVA_HOME=/usr/lib/jvm/java-8-openjdk-x64/
Check the value of $JAVA_HOME
echo $JAVA_HOME2-2. Install Visual Studio Code
https://code.visualstudio.com/docs/setup/linux
sudo snap install --classic code2-3. Install Maven
Apache Kafka Word Count – Java No.44 “2-3. Installing Apache Maven”
2-4. Install the latest version of MySQL
# Install mysql sudo apt-get update sudo apt-get install mysql-server # Start mysql service sudo systemctl start mysql # enable MySQL to start automatically when the machine is online sudo systemctl enable mysql
2-5. Download mysql java connector
After install of MySQL, mysql java connector is installed using the following commands.
Download mysql-connector-java_8.0.30-1ubuntu20.04_all.deb from MySQL :: Download Connector/J according to OS type.
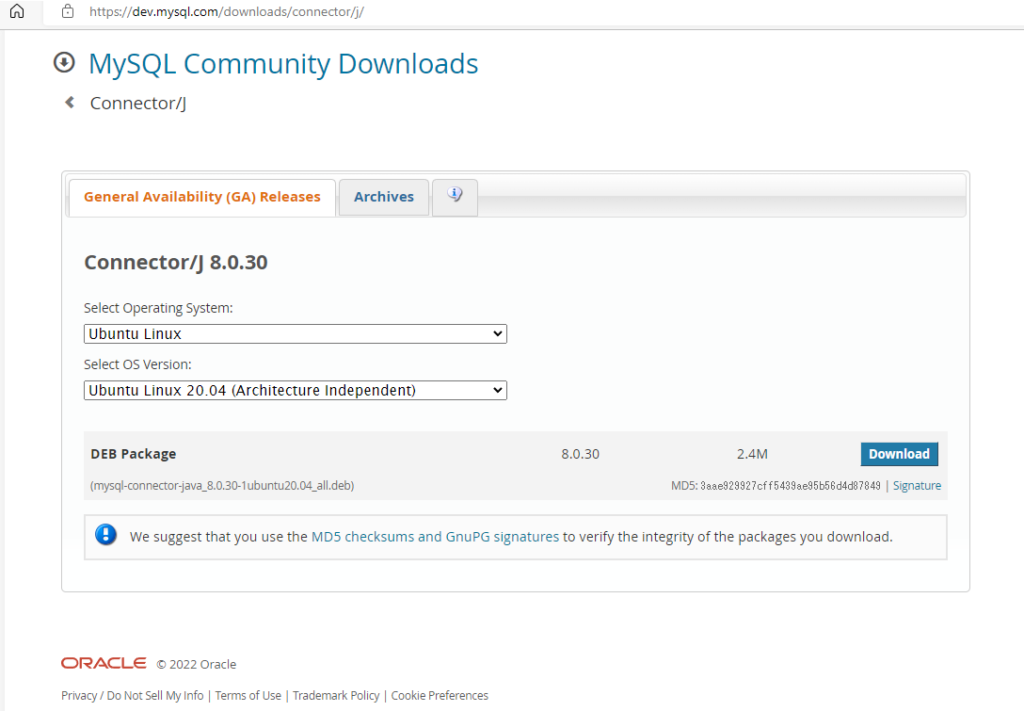
Click “Download” button and then Click ”No thanks, just start my download”.
2-6. Install mysql java connector
sudo apt install ./mysql-connector-java_8.0.30-1ubuntu20.04_all.deb
sudo ln -s /usr/share/java/mysql-connector-java-8.0.30.jar $HIVE_HOME/lib/mysql-connector-java.jar2-7. Create Database “testdb” and user “hiveuser”
Create Database “testdb” and user “hiveuser” with password “hivepassword” as test
# Connect to mysql using root user without password
sudo mysql -u root
# Change plugin to make root access to MySQL with password authentication.
mysql> USE mysql;
mysql> UPDATE user SET plugin='caching_sha2_password' WHERE User='root';
mysql> FLUSH PRIVILEGES;
mysql> select user,host,plugin from mysql.user;
mysql> exit;
# Restart mysql
sudo service mysql restart
# Create Database "testdb" and table "testtbl". after that, some records are inserted.
# Connect to mysql using root without password (Just press enter if password is required)
mysql -u root -p
# Create database "testdb"
mysql> CREATE DATABASE testdb;
mysql> USE testdb;
mysql> create table testtbl (c1 int, c2 int);
mysql> insert testtbl values(1,1),(2,2),(3,3);
mysql> select * from testtbl;
+------+------+
| c1 | c2 |
+------+------+
| 1 | 1 |
| 2 | 2 |
| 3 | 3 |
+------+------+
3 rows in set (0.00 sec)
# Create user "hiveuser" and passoward "hivepassword"
mysql> CREATE USER 'hiveuser'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED BY 'hivepassword';
mysql> GRANT all on *.* to 'hiveuser'@'localhost';
mysql> flush privileges;
mysql> exit;▼3. Connect to MySQL on Ubuntu and execute select query in Java
3-1. Create an Apache Maven project
mvn archetype:generate -DinteractiveMode=false -DgroupId=org.example.mysqlcon -DartifactId=mysqlconnection -DarchetypeArtiFactId=maven-archetype-quickstart3-2. Remove the existed both App.java and AppTest.java
rm ./mysqlconnection/src/main/java/org/example/mysqlcon/App.java
rm ./mysqlconnection/src/test/java/org/example/mysqlcon/AppTest.java 3-3. Start Visual Studio Code
cd ./mysqlconnection
code .3-4. Update pom.xml as below and save it (Ctrl+S)
<properties>
<project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding>
<maven.compiler.source>1.8</maven.compiler.source>
<maven.compiler.target>1.8</maven.compiler.target>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<version>8.0.30</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
<version>3.8.1</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</project>
3-5. Connect to MySQL and execute select query
Use Database “testdb” and user “hiveuser” with the password.
package org.example.mysqlcon;
import java.sql.*;
import java.util.logging.Level;
import java.util.logging.Logger;
public class mysqlcontest {
private static final Logger log;
private static final String DB_URL = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/testdb";
private static final String USER = "hiveuser";
private static final String PASSWORD = "hivepassword";
static {
log = Logger.getLogger(mysqlcontest.class.getName());
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws SQLException {
Connection conn = null;
Statement stmt = null;
// Register JDBC driver
try {
Class.forName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver");
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
log.log(Level.SEVERE, "Where is your MySQL JDBC Driver?", e);
return;
}
try {
// Register JDBC driver
Class.forName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver");
// pen a connection
log.log(Level.INFO, "Connecting to database...");
conn = DriverManager.getConnection(DB_URL, USER, PASSWORD);
// Execute a query
log.log(Level.INFO, "Creating statement...");
stmt = conn.createStatement();
String sql = "SELECT * FROM testtbl";
ResultSet rs = stmt.executeQuery(sql);
// Extract data from result set
while (rs.next()) {
// Retrieve by column name
int c1 = rs.getInt("c1");
int c2 = rs.getInt("c2");
// Display values
System.out.println("c1: " + c1 + ", c2: " + c2);
}
//Clean-up environment
rs.close();
} catch (SQLException se) {
// Handle errors for JDBC
se.printStackTrace();
} catch (Exception e) {
// Handle errors for Class.forName
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
// finally block used to close resources
try {
if (stmt != null)
stmt.close();
} catch (SQLException se2) {
} // nothing we can do
try {
if (conn != null)
conn.close();
} catch (SQLException se) {
se.printStackTrace();
} // end finally try
} // end try
log.log(Level.INFO, "Operation done successfully");
}
} 3-6. Results of this code
Nov 21, 2022 4:48:14 PM org.example.mysqlcon.mysqlcontest main INFO: Connecting to database... Nov 21, 2022 4:48:15 PM org.example.mysqlcon.mysqlcontest main INFO: Creating statement... c1: 1, c2: 1 c1: 2, c2: 2 c1: 3, c2: 3 Nov 21, 2022 4:48:15 PM org.example.mysqlcon.mysqlcontest main INFO: Operation done successfully
▼4. Reference
- MySQL https://dev.mysql.com/doc/refman/8.0/en/what-is-mysql.html
- VS Code https://code.visualstudio.com/docs/setup/linux
- Maven Install Apache Kafka Word Count 実装 – Java No.44 “2-3. Apache Maven” 参照
- Download mysql java connector MySQL :: Download Connector/J
That’s all. Have a nice day ahead !!!